How Long Does Food Last When Vacuum Sealed? Discover the power of vacuum sealing with FOODS.EDU.VN to extend food freshness, minimize waste, and optimize your kitchen. Dive into our comprehensive guide on preserving food through vacuum sealing, along with tips on extending storage duration, and maintaining high quality.
1. Understanding Vacuum Sealing for Food Preservation
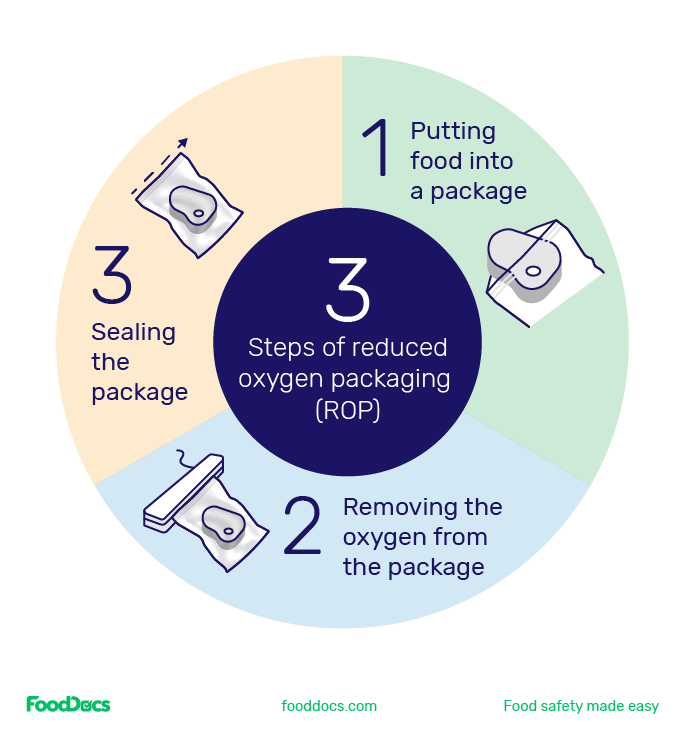
Vacuum sealing is a powerful food preservation technique that involves removing air from packaging before sealing it tightly. This process, also known as reduced oxygen packaging (ROP), inhibits the growth of aerobic bacteria and mold, significantly extending the shelf life of various foods. The absence of oxygen not only slows down spoilage but also helps to maintain the flavor, texture, and nutritional value of your ingredients. According to the USDA, vacuum sealing can extend the shelf life of some foods by as much as five times compared to traditional storage methods.
Vacuum sealing provides many benefits:
- Extended Shelf Life: By reducing oxygen exposure, vacuum sealing prevents spoilage and extends the freshness of food.
- Preserved Flavor and Texture: Vacuum sealing maintains the original taste and texture of food by preventing oxidation.
- Reduced Freezer Burn: Vacuum sealing eliminates air contact, which is a major cause of freezer burn.
- Efficient Storage: Vacuum sealed packages take up less space and can be organized more efficiently.
- Cost Savings: By extending the shelf life of food, vacuum sealing helps reduce food waste and save money.
For more in-depth knowledge on food preservation, explore the resources at FOODS.EDU.VN.
2. The Science Behind Vacuum Sealing and Food Spoilage
Food spoilage occurs when microorganisms, enzymes, and oxidation degrade the quality and safety of food. Aerobic bacteria, molds, and yeasts thrive in oxygen-rich environments, leading to unpleasant odors, flavors, and textures. Enzymes naturally present in food can also cause deterioration over time, while oxidation can result in discoloration and rancidity. Vacuum sealing combats these processes by removing oxygen, creating an environment that is unfavorable for most spoilage organisms.
Key Spoilage Factors:
- Microbial Growth: Aerobic bacteria need oxygen to grow and spoil food.
- Enzymatic Activity: Enzymes can degrade food quality over time.
- Oxidation: Oxygen causes rancidity and discoloration in fats and certain foods.
According to a study published in the Journal of Food Science, vacuum sealing significantly reduces microbial growth and enzymatic activity in various food products, leading to extended shelf life and improved quality retention.
3. How Vacuum Sealing Extends Food Shelf Life: A Detailed Look
Vacuum sealing is not a one-size-fits-all solution. The shelf life extension depends on the type of food, its initial condition, and storage temperature. Here’s a detailed breakdown of how vacuum sealing affects different food categories:
3.1. Meats and Poultry
Vacuum sealing dramatically increases the shelf life of meats and poultry by preventing oxidation and microbial growth. Here’s a comparison:
| Type of Meat | Refrigerated (Unsealed) | Refrigerated (Vacuum Sealed) | Frozen (Unsealed) | Frozen (Vacuum Sealed) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beef | 3-5 days | 10-14 days | 6 months | 1-3 years |
| Pork | 3-5 days | 8-12 days | 4-6 months | 1 year |
| Chicken/Turkey | 1-2 days | 5-7 days | 9 months | 1 year |
| Ground Meat | 1-2 days | 3-5 days | 3-4 months | 9-12 months |
| Processed Meats | 7 days | 14-21 days | 1-2 months | 6-12 months |
Key Points:
- Vacuum sealing raw meat can extend its refrigerated shelf life by up to two weeks.
- Frozen vacuum sealed meats can last for years without significant quality loss.
- Always check for signs of spoilage, such as off odors or discoloration, before cooking.
For more tips on meat storage and handling, visit FOODS.EDU.VN.
3.2. Seafood
Seafood is highly perishable due to its high moisture content and enzymatic activity. Vacuum sealing can significantly extend its shelf life:
| Type of Seafood | Refrigerated (Unsealed) | Refrigerated (Vacuum Sealed) | Frozen (Unsealed) | Frozen (Vacuum Sealed) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fish | 1-2 days | 4-7 days | 6 months | 9-12 months |
| Shrimp | 1-2 days | 3-5 days | 3-6 months | 6-9 months |
| Shellfish | 1-2 days | 3-5 days | 2-3 months | 3-6 months |
Key Points:
- Vacuum sealing helps prevent freezer burn and maintain the delicate texture of seafood.
- Always ensure seafood is fresh before vacuum sealing to maximize its shelf life.
- Consult FOODS.EDU.VN for detailed guides on selecting and storing fresh seafood.
3.3. Fruits and Vegetables
The impact of vacuum sealing on fruits and vegetables varies depending on their type and respiration rate. Low-moisture vegetables like carrots and potatoes benefit greatly, while high-moisture items like lettuce may not.
| Type of Produce | Refrigerated (Unsealed) | Refrigerated (Vacuum Sealed) | Frozen (Unsealed) | Frozen (Vacuum Sealed) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Berries | 1-3 days | 5-7 days | 6-12 months | 1-2 years |
| Leafy Greens | 3-7 days | 7-10 days | N/A | N/A |
| Root Vegetables | 2-3 weeks | 1-2 months | 8-12 months | 1-2 years |
| Cut Fruits | 1-2 days | 3-5 days | 2-3 months | 6-8 months |
Key Points:
- Blanching vegetables before vacuum sealing can help preserve their color, flavor, and texture.
- Some fruits and vegetables may become mushy when vacuum sealed due to their high water content.
- FOODS.EDU.VN offers expert advice on preparing and storing different types of produce.
3.4. Dairy Products
Vacuum sealing can help extend the shelf life of certain dairy products, especially hard cheeses:
| Type of Dairy | Refrigerated (Unsealed) | Refrigerated (Vacuum Sealed) | Frozen (Unsealed) | Frozen (Vacuum Sealed) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hard Cheese | 2-4 weeks | 4-8 weeks | 6 months | 1 year |
| Soft Cheese | 1-2 weeks | 2-4 weeks | N/A | N/A |
| Butter | 1-3 months | 3-6 months | 6-9 months | 1 year |
Key Points:
- Vacuum sealing helps prevent mold growth and flavor deterioration in hard cheeses.
- Soft cheeses may not benefit as much from vacuum sealing due to their high moisture content.
- For detailed insights on dairy storage, explore FOODS.EDU.VN.
3.5. Cooked Foods
Vacuum sealing cooked foods can extend their refrigerated shelf life, making meal prepping more convenient:
| Type of Cooked Food | Refrigerated (Unsealed) | Refrigerated (Vacuum Sealed) | Frozen (Unsealed) | Frozen (Vacuum Sealed) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cooked Meats | 3-4 days | 7-10 days | 2-3 months | 6-12 months |
| Cooked Vegetables | 3-4 days | 5-7 days | 2-3 months | 6-8 months |
| Soups/Stews | 3-4 days | 6-8 days | 2-3 months | 6-8 months |
Key Points:
- Allow cooked foods to cool completely before vacuum sealing to prevent condensation and bacterial growth.
- Vacuum sealing can help maintain the flavor and texture of cooked foods during storage.
- FOODS.EDU.VN provides a wealth of information on safe food handling and storage practices.
4. Vacuum Sealing Techniques: Step-by-Step Guide
Mastering the art of vacuum sealing ensures optimal food preservation and safety. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Prepare the Food: Ensure food is fresh, clean, and properly trimmed. Cut into appropriate portions for storage.
- Choose the Right Bags: Select vacuum sealing bags that are appropriate for the type of food and your vacuum sealer.
- Fill the Bag: Place the food inside the bag, leaving enough space at the top for sealing.
- Seal the Bag: Follow the manufacturer’s instructions to vacuum seal the bag, removing as much air as possible.
- Label and Date: Clearly label the bag with the contents and date of sealing to track shelf life.
- Store Properly: Store vacuum sealed foods in the refrigerator or freezer at the appropriate temperature.
Tips for Effective Vacuum Sealing:
- Ensure the sealing surface is clean and dry for a strong seal.
- Avoid overfilling bags to ensure proper sealing.
- For powdery or granular foods, consider using a bag with a filter to prevent clogging the vacuum sealer.
5. Addressing Common Concerns and Misconceptions About Vacuum Sealing
Vacuum sealing is often surrounded by myths and misunderstandings. Let’s address some common concerns:
-
Myth: Vacuum sealing eliminates all risks of food spoilage.
- Fact: Vacuum sealing slows down spoilage but does not eliminate it entirely. Some bacteria, like Clostridium botulinum, can grow in low-oxygen environments.
-
Myth: Vacuum sealing can revive spoiled food.
- Fact: Vacuum sealing can only preserve the quality of fresh food; it cannot reverse spoilage.
-
Myth: All foods benefit equally from vacuum sealing.
- Fact: Some foods, like soft fruits and vegetables, may not benefit as much from vacuum sealing due to their high moisture content.
For more clarity on food safety and preservation, turn to the experts at FOODS.EDU.VN.
6. Safety Considerations: Botulism and Vacuum Sealing
While vacuum sealing extends shelf life, it’s crucial to be aware of the risks of Clostridium botulinum, the bacteria responsible for botulism. This anaerobic bacterium thrives in low-oxygen environments and can produce a deadly toxin.
Preventing Botulism:
- Refrigerate Properly: Store vacuum sealed foods at temperatures below 40°F (4°C) to inhibit bacterial growth.
- Blanch Vegetables: Blanching vegetables before vacuum sealing can destroy enzymes and reduce the risk of bacterial contamination.
- Follow Guidelines: Adhere to recommended storage times and temperatures for vacuum sealed foods.
- Be Vigilant: Discard any vacuum sealed food that shows signs of spoilage, such as bulging bags, off odors, or discoloration.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), proper refrigeration and handling are essential to prevent botulism in vacuum sealed foods.
7. Vacuum Sealing and HACCP: Ensuring Food Safety in Commercial Settings
In commercial food operations, vacuum sealing requires a Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) plan to ensure food safety compliance. A HACCP plan identifies potential hazards and implements control measures to prevent foodborne illnesses.
Key Components of a HACCP Plan for Vacuum Sealing:
- Hazard Analysis: Identify potential hazards, such as bacterial growth, and assess their risks.
- Critical Control Points (CCPs): Determine critical control points, such as refrigeration temperature and sealing process.
- Critical Limits: Establish critical limits, such as maximum storage time and minimum refrigeration temperature.
- Monitoring Procedures: Implement monitoring procedures to ensure critical limits are met.
- Corrective Actions: Define corrective actions to take if critical limits are exceeded.
- Verification Procedures: Establish verification procedures to ensure the HACCP plan is effective.
- Record-Keeping: Maintain accurate records of monitoring activities and corrective actions.
FOODS.EDU.VN offers comprehensive resources and templates to help food businesses develop and implement effective HACCP plans.
8. Best Vacuum Sealing Machines for Home and Commercial Use
Selecting the right vacuum sealing machine is crucial for achieving optimal results. Here are some top-rated options for home and commercial use:
| Type of Machine | Features | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Handheld Sealers | Compact, portable, easy to use | Affordable, space-saving, suitable for small quantities | Less powerful, limited functionality |
| External Sealers | Versatile, suitable for various bag sizes, adjustable settings | More powerful, versatile, suitable for frequent use | Bulkier, requires special bags |
| Chamber Sealers | Professional-grade, high-powered, suitable for liquids | Provides the best seal, suitable for commercial use, handles liquids | Expensive, bulky, requires more maintenance |
Top Brands:
- FoodSaver: Known for reliability and ease of use.
- Seal-a-Meal: Offers affordable options for home use.
- VacMaster: Provides professional-grade machines for commercial applications.
9. Sustainable Vacuum Sealing: Eco-Friendly Options
As consumers become more environmentally conscious, sustainable vacuum sealing options are gaining popularity. Here are some eco-friendly alternatives:
- Reusable Bags: Made from durable, BPA-free materials, reusable bags can be washed and reused multiple times.
- Compostable Bags: Made from plant-based materials, compostable bags can be composted in industrial composting facilities.
- Recyclable Bags: Some vacuum sealing bags are made from recyclable materials, reducing their environmental impact.
By choosing sustainable vacuum sealing options, you can reduce your carbon footprint and contribute to a more sustainable food system.
10. The Future of Food Preservation: Innovations in Vacuum Sealing Technology
The field of food preservation is constantly evolving, with ongoing innovations in vacuum sealing technology. Some exciting developments include:
- Modified Atmosphere Packaging (MAP): MAP involves altering the gas composition inside the packaging to further extend shelf life and preserve food quality.
- Smart Packaging: Smart packaging incorporates sensors and indicators to monitor food freshness and safety in real-time.
- Antimicrobial Packaging: Antimicrobial packaging contains antimicrobial agents that inhibit bacterial growth and extend shelf life.
These advancements promise to revolutionize food preservation, making it safer, more efficient, and more sustainable. Stay updated with the latest trends and technologies at FOODS.EDU.VN.
FAQ: Common Questions About Vacuum Sealing
-
Can I vacuum seal hot foods?
- It’s best to let hot foods cool completely before vacuum sealing to prevent condensation and bacterial growth.
-
Can I reuse vacuum sealing bags?
- Reusable vacuum sealing bags can be washed and reused. However, bags that have contained raw meat, poultry, or fish should be discarded.
-
How do I prevent moisture from being sucked into the vacuum sealer?
- Freeze foods for a short period before vacuum sealing, or place a paper towel inside the bag to absorb excess moisture.
-
Is it safe to vacuum seal cheese?
- Yes, vacuum sealing can help extend the shelf life of hard cheeses. However, soft cheeses may not benefit as much from vacuum sealing.
-
What foods should not be vacuum sealed?
- Certain vegetables, like broccoli, cauliflower, and cabbage, should be blanched before vacuum sealing to prevent enzyme activity. Soft fruits and vegetables may become mushy when vacuum sealed.
-
How long does vacuum sealed meat last in the freezer?
- Vacuum sealed meat can last up to 1-3 years in the freezer without significant quality loss.
-
What are the signs of spoiled vacuum sealed food?
- Signs of spoilage include bulging bags, off odors, discoloration, and a slimy texture.
-
Can vacuum sealing prevent freezer burn?
- Yes, vacuum sealing eliminates air contact, which is a major cause of freezer burn.
-
Do I need a special vacuum sealer for liquids?
- Chamber vacuum sealers are best for sealing liquids, as they prevent the liquid from being sucked into the machine.
-
Where can I find reliable information about vacuum sealing and food safety?
- FOODS.EDU.VN offers a wealth of information on vacuum sealing, food safety, and HACCP plans.
Vacuum sealing is an invaluable tool for extending food shelf life, reducing waste, and saving money. By following best practices and staying informed about the latest innovations, you can maximize the benefits of this powerful food preservation technique.
Ready to dive deeper into the world of culinary expertise? Visit FOODS.EDU.VN today for a treasure trove of recipes, cooking tips, and in-depth guides on everything from sous vide to molecular gastronomy. Don’t just cook—create with FOODS.EDU.VN!
Address: 1946 Campus Dr, Hyde Park, NY 12538, United States
Whatsapp: +1 845-452-9600
Website: foods.edu.vn